barisozmen.github.io
System Design Resources
System design of Twitter
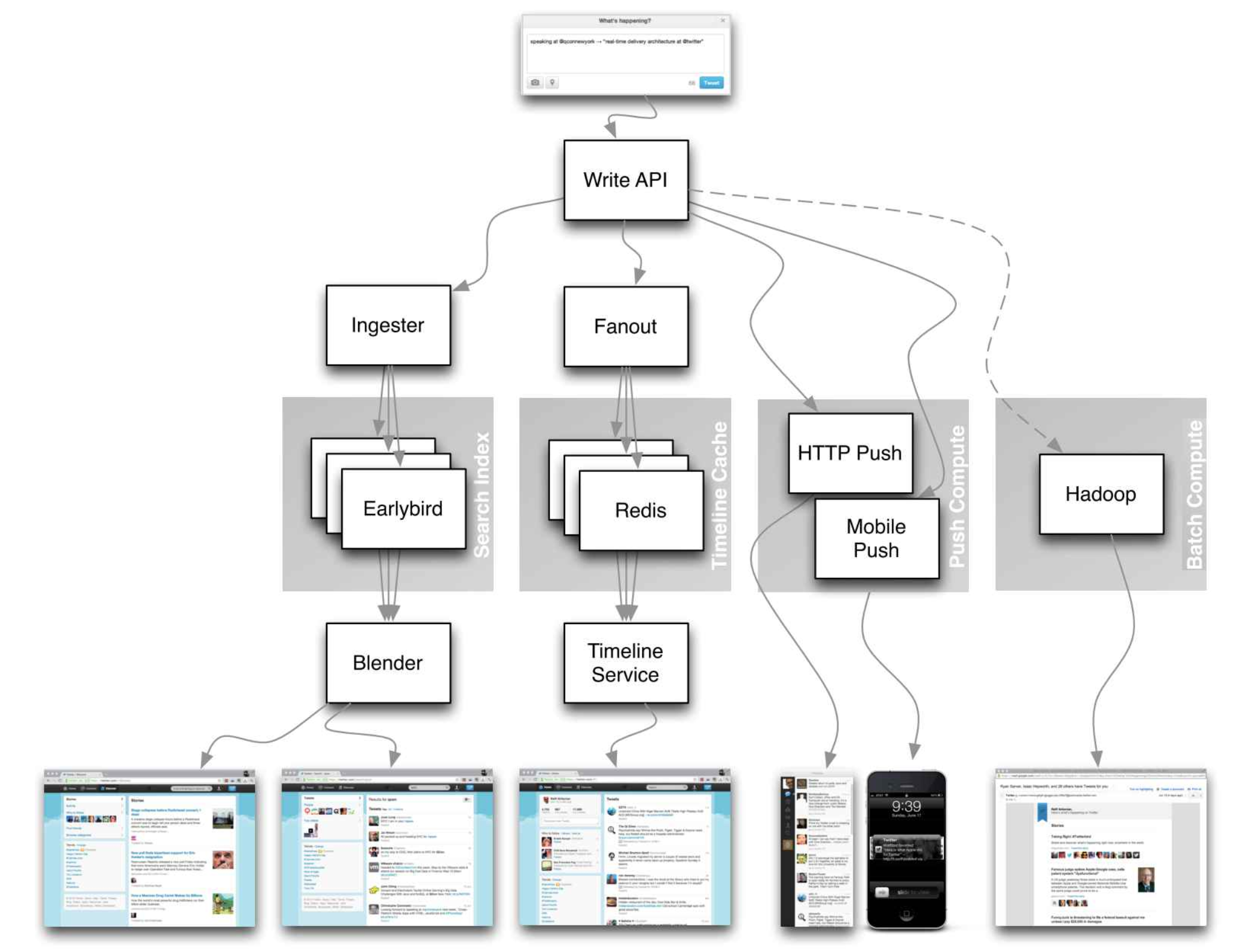 source: https://www.infoq.com/presentations/Twitter-Timeline-Scalability
source: https://www.infoq.com/presentations/Twitter-Timeline-Scalability
Everything-in-it page
https://github.com/donnemartin/system-design-primer
Interview solutions
- How to design…
- General:
- Top 10 System Desing Questions (hackernoon)
- A good GitHub page
Real-world examples (Tech Engineering pages)
Resource with many real-world system design explanations: http://highscalability.com/
- Yelp: https://engineeringblog.yelp.com/2016/07/billions-of-messages-a-day-yelps-real-time-data-pipeline.html
- Netflix: https://medium.com/netflix-techblog/evolution-of-the-netflix-data-pipeline-da246ca36905
- AirBnb: https://medium.com/@airbnbeng
- Facebook:
- Pinterest: medium
- Twitter:
- Uber: engineering website
- Dropbox: Video: How we’ve scaled dropbox
Step-by-step
- Requirements classification
- System interface definition
- Back-of-the-envelope estimation
- Defining data model
- High-level design
- Detailed design
- Identifying and resolving bottlenecks
Very good course
Grokking the system design interview
Great book
Distributed systems for fun and profit
Some terms
Introduction to architecting systems for scale
https://lethain.com/introduction-to-architecting-systems-for-scale/
- Load balancing
- Smart clients
- Hardware load balancers
- Software load balancers
- Caching
- Off-line processing
- Message queues
- Tool: RabbitMQ
- Scheduling periodic tasks
- MapReduce
- Tool: Hadoop MapReduce, Hive, HBase
- Platform Layer
- Message queues
HTTP requests
https://www.codecademy.com/articles/http-requests
- HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol
- TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
- URL: Uniform Resource Locator
- HTTP verbs:
- GET — retrieve a specific resource (by id) or a collection of resources
- POST — create a new resource
- PUT — update a specific resource (by id)
- DELETE — remove a specific resource by id
- List of HTTP status codes
What is REST
https://www.codecademy.com/articles/what-is-rest
- REST: REpresentational State Transfer
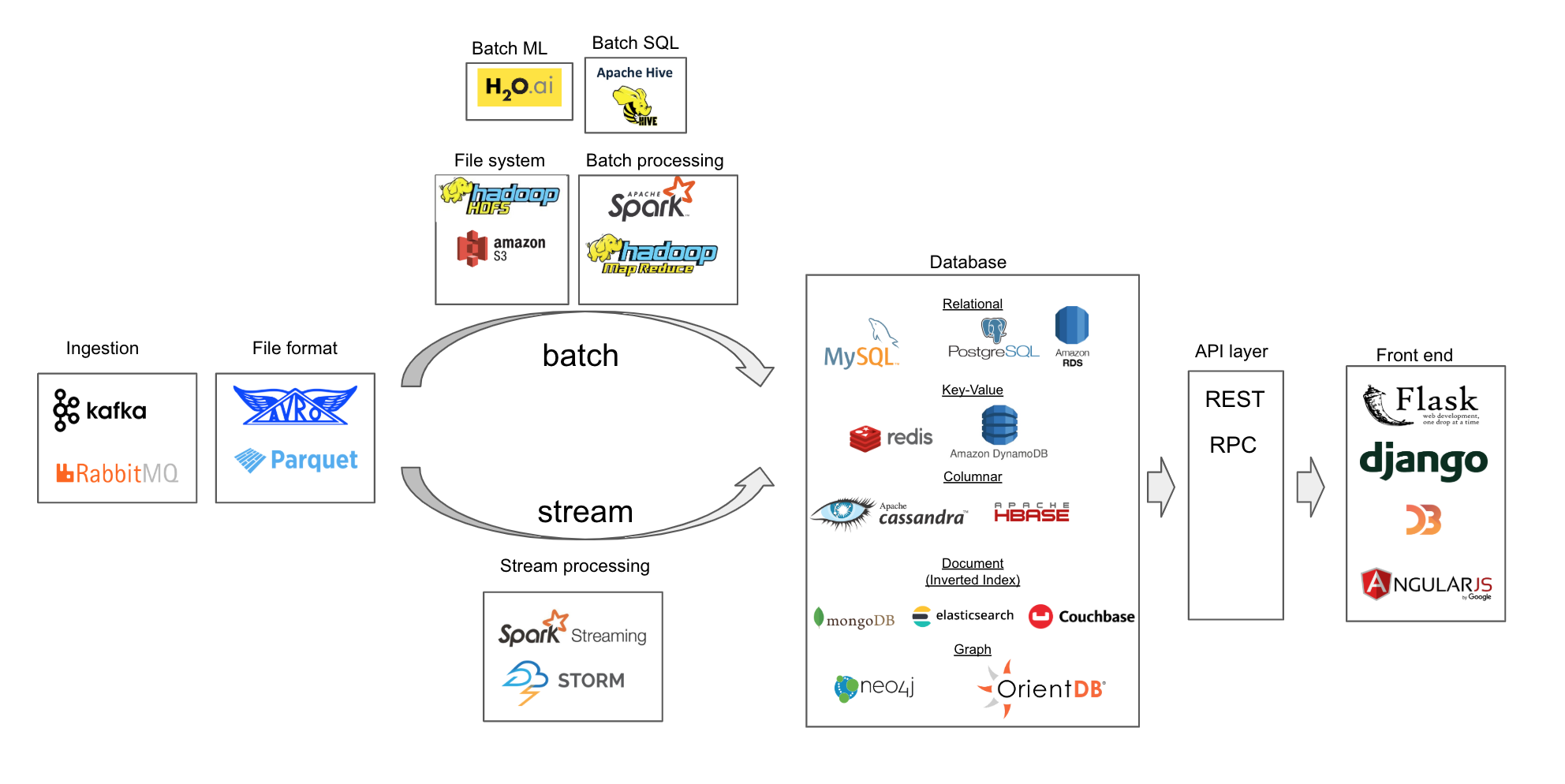
Data engineering pipeline
with choices of technologies for each stage
CAP Theorem

In a distributed computer system, you can only support two of the following guarantees:
Consistency - Every read receives the most recent write or an error
Availability - Every request receives a response, without guarantee that it contains the most recent version of the information
Partition Tolerance - The system continues to operate despite arbitrary partitioning due to network failures Networks aren’t reliable, so you’ll need to support partition tolerance. You’ll need to make a software tradeoff between consistency and availability.
Consistent Hashing
A hash map with machines instead of buckets (ref).